©2015 -



Information Technology



Installing SQL Server 2008 R2 In Windows Server 2012 R2 -
At Feature Selection, click [select all]
Default directories -
Shared feature dir: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server
Shared feature dir (x86): C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server
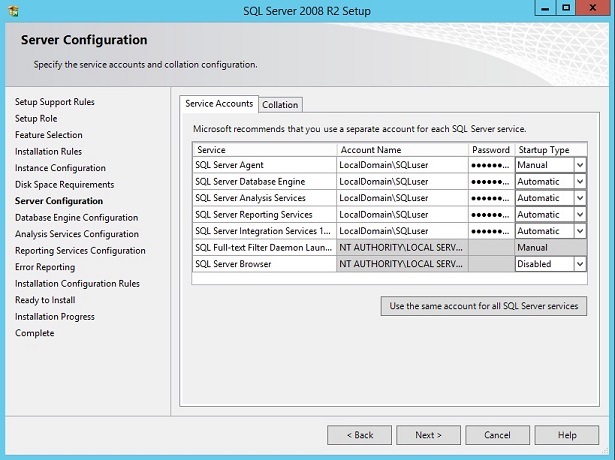
Service Account tab, Microsoft recommends that you use separate accounts for each SQL Server service.
But in our case since this is a lab, I'll set everything as one user for each of the services below.
SQL Server Agent (startup mode: manual)
SQL Server Database Engine (startup mode: auto)
SQL Server Analysis Services (startup mode: auto)
SQL Server Reporting Services (startup mode: auto)
SQL Server Integration Services (startup mode: auto)
-
NOTE: select [browse] to search for the user SQLuser which I created previously.
Account name: LocalDomain\SQLuser
Password: ******
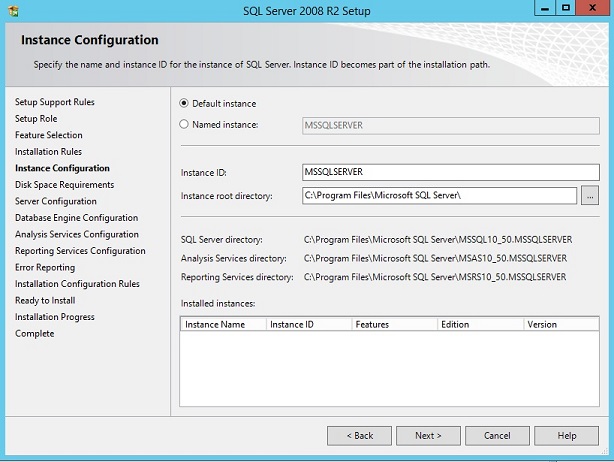
Select Default Instance.
Instance name: MSSQLSERVER
Instance ID: MSSQLSERVER
Instance root dir: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server
If there are other instances running on the same box perhaps also of different version, you may select Named Instance to give it a unique name.
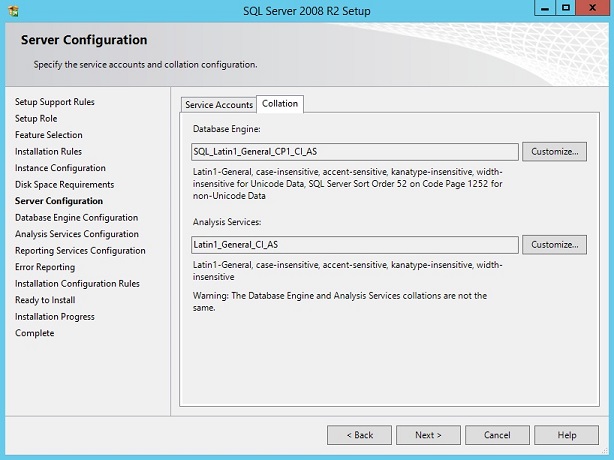
The Collation tab provides you the option to choose the supported language type for both Database Engine and Analysis Services.
In my case, I set everything as default.
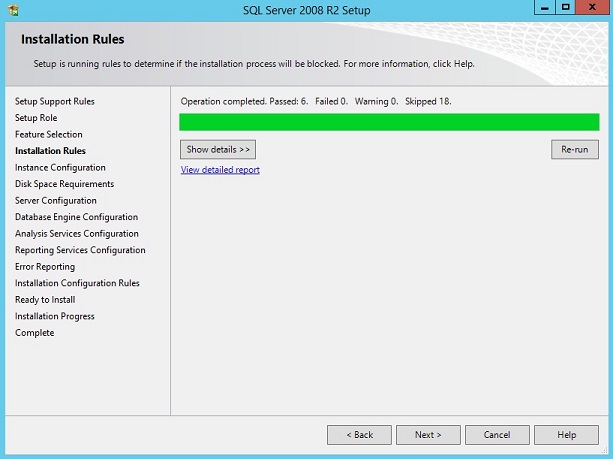
Based on the previous selection of SQL Server Features, a report is generated and should give you "Failed 0" and "Warning 0".
Click [next] if all is looking good.
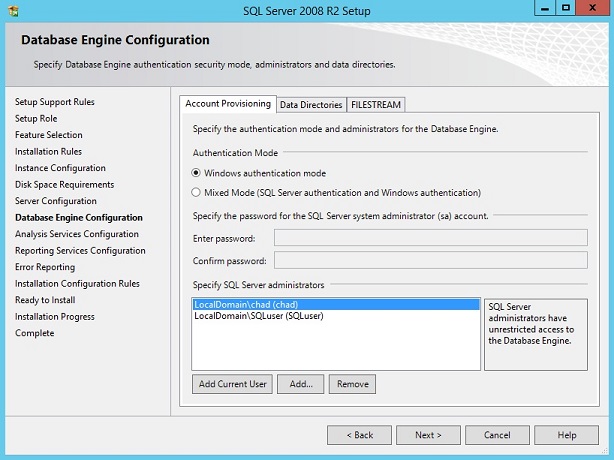
VII. Database Engine Configuration
At Account Provisioning tab, select Windows authentication mode. This means that login users defined as SQL Server administrators are good enough to administer the database engine. In my case, I added a few users.